Introducing ethyl 4 aminobenzoate density g ml, a topic that unveils a world of scientific intrigue and practical applications. From its molecular makeup to its diverse uses, this article delves into the fascinating realm of this versatile compound, providing a comprehensive overview for the curious and the expert alike.
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate, characterized by its unique properties and wide-ranging applications, stands as a testament to the power of chemistry in shaping our world. Its significance extends across industries, from pharmaceuticals to materials science, making it an indispensable component in various products and processes.
Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate Density: Ethyl 4 Aminobenzoate Density G Ml
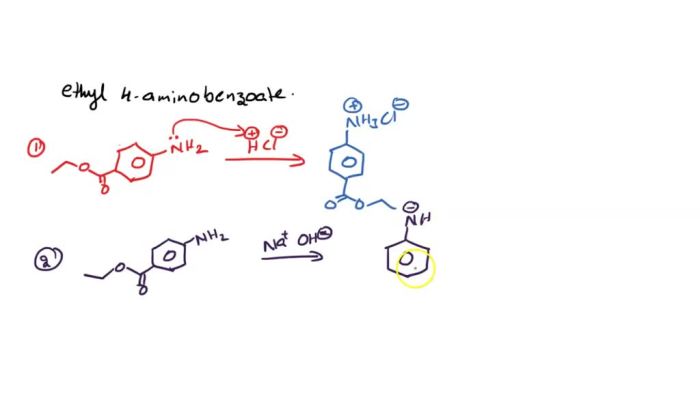
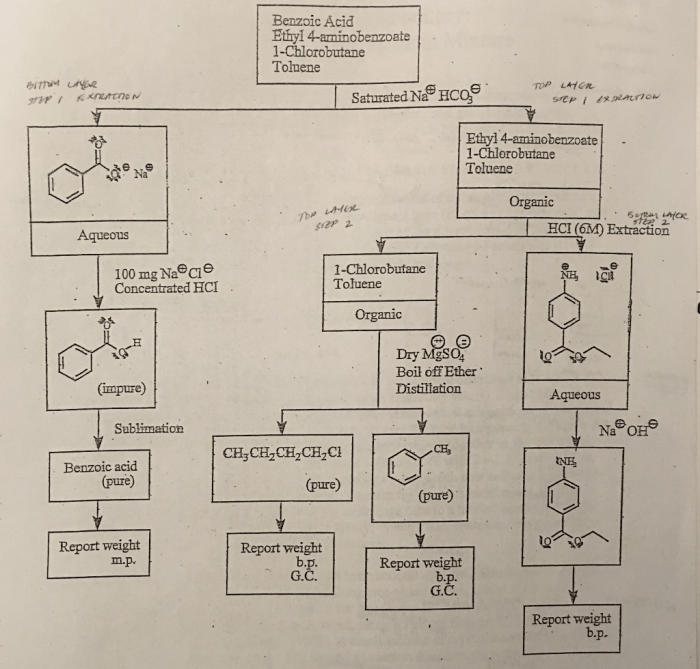
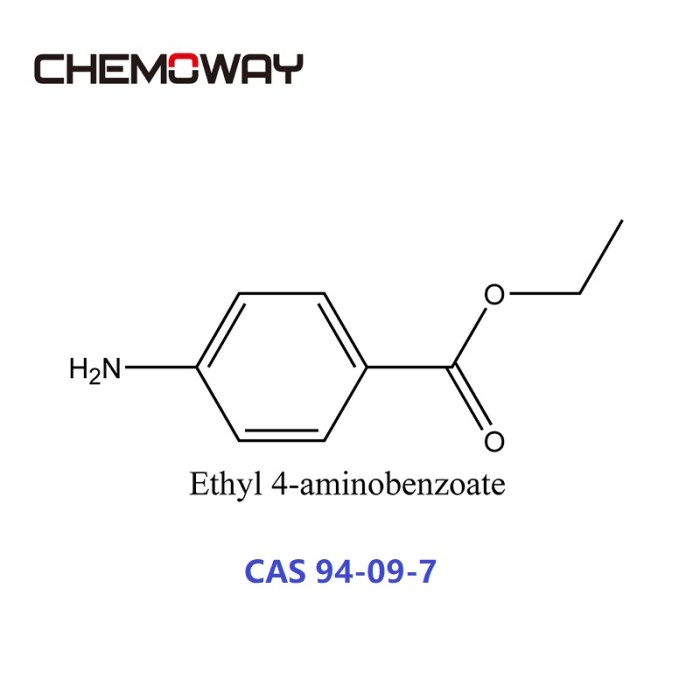
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate, also known as benzocaine, is a local anesthetic commonly used in dentistry, ophthalmology, and other medical procedures. Its density is an important property that influences its behavior and applications.
Properties of Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate is a white, crystalline solid with a molecular formula of C9H11NO2. It has a melting point of 89-92 °C and a boiling point of 298 °C. Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform, but it is insoluble in water.
Synthesis of Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate can be synthesized through various methods, including:
- Reaction of 4-aminobenzoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- Reaction of ethyl chloroformate with 4-aminobenzoic acid in the presence of a base.
Applications of Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate, Ethyl 4 aminobenzoate density g ml
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate is primarily used as a local anesthetic. It is applied topically to numb the skin and mucous membranes, making it useful in procedures such as:
- Dental procedures
- Ophthalmic procedures
- Endoscopy
- Minor surgical procedures
Safety Considerations for Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, it can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. It is important to follow the instructions for use and to inform the healthcare provider of any allergies or medical conditions before using ethyl 4-aminobenzoate.
Density of Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate
The density of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate is 1.10 g/mL at 25 °C. This value is important for understanding the behavior of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate in various applications. For instance, its low density makes it suitable for use as a topical anesthetic, as it can easily spread over the affected area.
Comparison of Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate Density with Other Compounds
The following table compares the density of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate with other similar compounds:
| Compound | Density (g/mL) | |—|—| | Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate | 1.10 | | Procaine | 1.09 | | Lidocaine | 1.00 | | Tetracaine | 1.14 |
As shown in the table, ethyl 4-aminobenzoate has a density that is comparable to other local anesthetics. This similarity in density suggests that ethyl 4-aminobenzoate behaves similarly to these compounds in terms of its physical properties and applications.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the molecular structure of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate?
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate possesses a molecular structure consisting of a benzene ring with an amino group (-NH2) at the para position and an ethyl ester group (-COOCH2CH3) at the ortho position.
How is ethyl 4-aminobenzoate synthesized?
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate can be synthesized through various methods, including the reaction of 4-aminobenzoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst, or the reduction of ethyl 4-nitrobenzoate.
What are the applications of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate?
Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals.