The International Building Code (IBC) 2018 sets forth comprehensive requirements for tempered glass, a crucial building material that enhances safety and performance in various applications. This article delves into the intricacies of IBC 2018 tempered glass requirements, exploring its composition, safety considerations, design factors, and installation guidelines.
Tempered glass, renowned for its exceptional strength and shatter resistance, plays a vital role in modern architecture. Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for shower enclosures, windows, doors, and other applications where safety and durability are paramount.
Tempered Glass Definition and Composition: Ibc 2018 Tempered Glass Requirements
Tempered glass, also known as toughened glass, is a type of safety glass that undergoes a controlled thermal treatment process to enhance its strength and durability. It is composed of annealed glass that has been heated to a high temperature (approximately 620°C or 1150°F) and then rapidly cooled with jets of cold air.
This process creates a surface layer of tempered glass that is under compression, while the interior remains in tension. The result is a glass that is four to five times stronger than regular annealed glass and has increased resistance to breakage and impact.
Manufacturing Process and Heat Treatment
The manufacturing process of tempered glass involves several stages. First, the glass is cut to the desired size and shape. It is then heated in a tempering oven until it reaches its softening point. The glass is then rapidly cooled with jets of cold air, which causes the surface to cool faster than the interior.
This creates a compressive stress on the surface of the glass, while the interior remains in tension. The resulting glass is stronger and more resistant to breakage.
IBC 2018 Code Requirements for Tempered Glass
The International Building Code (IBC) 2018 sets forth specific requirements for the use of tempered glass in buildings. These requirements are intended to ensure the safety and durability of glass installations.
Specific Sections and Clauses, Ibc 2018 tempered glass requirements
The IBC 2018 addresses tempered glass in several sections and clauses, including:
- Section 2406.4.1: Safety glazing materials
- Section 2406.4.2: Tempered glass
- Section 2406.4.3: Laminated glass
- Section 2406.4.4: Wired glass
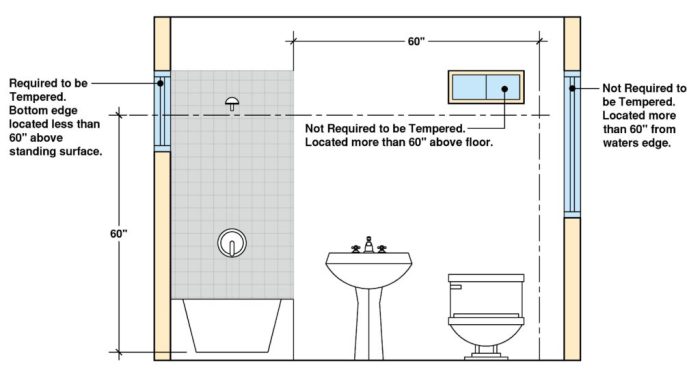
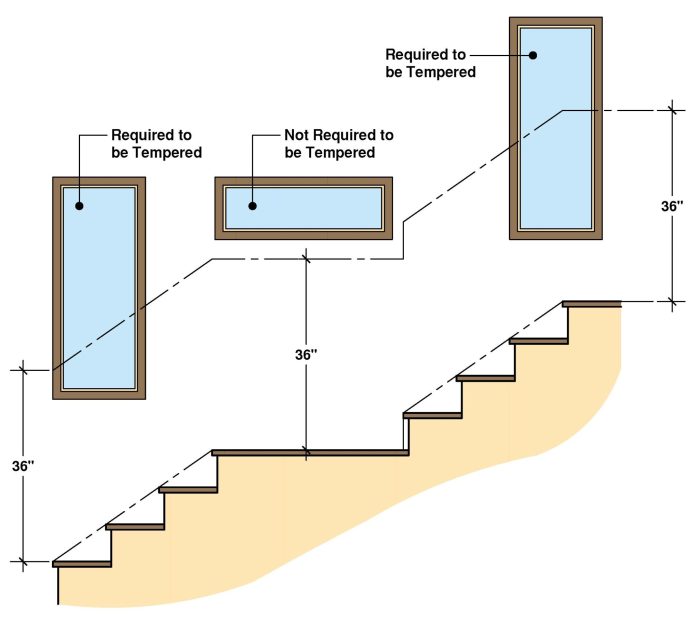
These sections and clauses provide detailed specifications for the use of tempered glass in various applications, such as shower enclosures, windows, and doors.
Safety Considerations and Applications
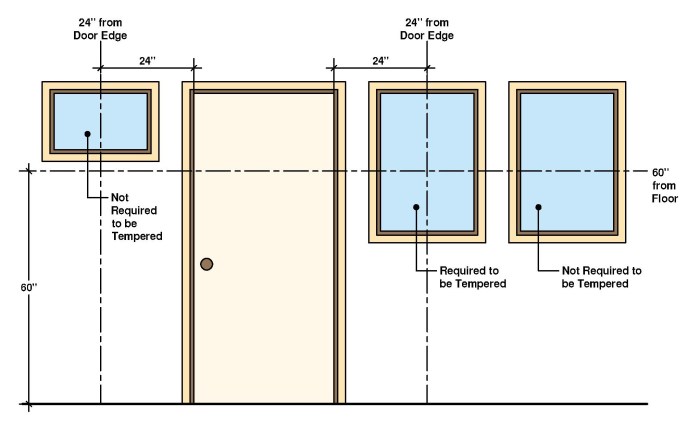
Tempered glass offers several safety benefits, including:
- Increased strength: Tempered glass is four to five times stronger than regular annealed glass, making it more resistant to breakage and impact.
- Shatter resistance: When tempered glass breaks, it shatters into small, relatively harmless fragments, reducing the risk of injury.
Due to its safety benefits, tempered glass is commonly used in applications where there is a risk of breakage or impact, such as:
- Shower enclosures
- Windows
- Doors
- Tabletops
- Vehicle windows
Testing and Certification
To ensure that tempered glass meets the IBC requirements, it must undergo rigorous testing. The most common test method is the ASTM C1048 standard, which involves subjecting the glass to a series of impact tests to assess its strength and shatter resistance.
Certification Programs and Organizations
Several organizations offer certification programs for tempered glass manufacturers. These programs verify that the glass meets the required safety standards. Some of the most recognized certification organizations include:
- Architectural Glass and Metal Certification Council (AGMCC)
- National Glass Association (NGA)
- Intertek
Design Considerations for Tempered Glass
When using tempered glass in buildings, there are several design factors to consider:
Thickness
The thickness of the tempered glass will determine its strength and resistance to breakage. The thicker the glass, the stronger it will be.
Edge Treatments
The edges of tempered glass must be properly treated to prevent chipping or breaking. Common edge treatments include grinding, polishing, and beveling.
Hardware Compatibility
The hardware used to install tempered glass must be compatible with the glass’s strength and thickness. The hardware should be able to withstand the forces that will be applied to the glass.
Installation and Maintenance
Tempered glass requires proper installation and maintenance to ensure its safety and durability.
Installation
Tempered glass should be installed by qualified professionals who are familiar with the proper handling and installation techniques.
Maintenance
Tempered glass should be cleaned regularly with a mild detergent and water. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or harsh chemicals, as these can damage the glass.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary benefit of using tempered glass?
Tempered glass offers exceptional strength and shatter resistance, making it less likely to break into sharp shards upon impact, enhancing safety.
How does the IBC 2018 address tempered glass requirements?
IBC 2018 provides specific sections and clauses that Artikel the requirements for tempered glass, including thickness, edge treatments, and hardware compatibility.
What are some common applications of tempered glass?
Tempered glass is commonly used in shower enclosures, windows, doors, storefronts, and other applications where safety and durability are essential.