Amendments worksheet bill of rights 1 10 – Embarking on an exploration of the Amendments Worksheet: Bill of Rights 1-10, this comprehensive guide delves into the profound significance of these constitutional amendments, meticulously crafted to safeguard the fundamental freedoms and liberties of American citizens. These first ten amendments, known collectively as the Bill of Rights, serve as the cornerstone of American jurisprudence, embodying the principles of individual liberty, due process, and limited government that have shaped the nation’s legal and political landscape for centuries.
As we navigate this discourse, we will examine each amendment in depth, exploring its historical context, legal implications, and enduring impact on American society. From the indispensable freedoms of speech and religion enshrined in the First Amendment to the vital protections against unreasonable searches and seizures Artikeld in the Fourth Amendment, this analysis will illuminate the intricate web of rights and responsibilities that define the American constitutional framework.
1. Introduction: Amendments Worksheet Bill Of Rights 1 10
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These amendments were adopted in 1791 and guarantee certain fundamental rights and freedoms to the American people. The Bill of Rights is considered to be one of the most important documents in American history, and it has been used to protect the rights of individuals from government overreach.
The first ten amendments to the Constitution are as follows:
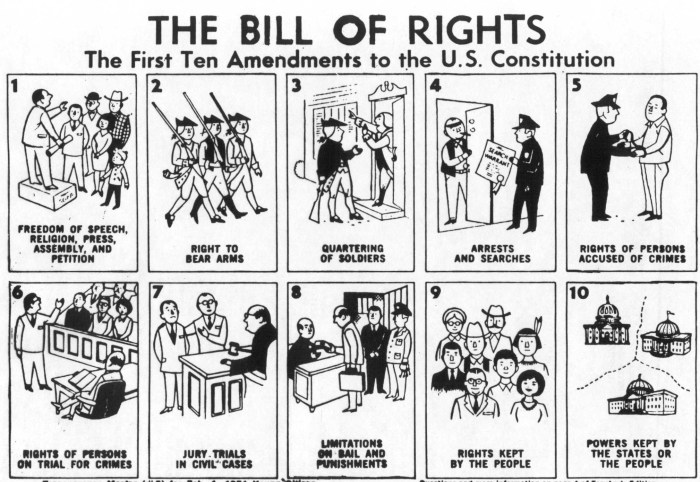
- Amendment 1: Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, and Petition
- Amendment 2: Right to Bear Arms
- Amendment 3: Quartering of Soldiers
- Amendment 4: Search and Seizure
- Amendment 5: Due Process and Self-Incrimination
- Amendment 6: Right to a Fair Trial
- Amendment 7: Right to a Jury Trial in Civil Cases
- Amendment 8: Excessive Bail and Cruel and Unusual Punishment
- Amendment 9: Rights Retained by the People
- Amendment 10: Powers Reserved to the States
2. Amendment 1
Freedom of Religion, Speech, Press, Assembly, and Petition
The First Amendment to the Constitution guarantees the freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, and petition. These freedoms are essential to a democratic society, and they allow individuals to express their beliefs and ideas without fear of government censorship.
The freedom of religion means that individuals are free to practice any religion they choose, or no religion at all. The government cannot establish an official religion or favor one religion over another.
The freedom of speech means that individuals are free to express their opinions and ideas without fear of government censorship. The government cannot prevent individuals from speaking out against the government or criticizing public officials.
The freedom of the press means that newspapers, magazines, and other media outlets are free to publish information without fear of government censorship. The government cannot prevent the media from reporting on controversial topics or criticizing the government.
The freedom of assembly means that individuals are free to gather together in groups to discuss issues or express their opinions. The government cannot prevent individuals from assembling peacefully, even if the government disagrees with their views.
The freedom of petition means that individuals are free to petition the government for redress of grievances. The government cannot prevent individuals from submitting petitions to the government, even if the government disagrees with their demands.
3. Amendment 2
Right to Bear Arms
The Second Amendment to the Constitution guarantees the right of individuals to keep and bear arms. This right is essential for self-defense and for the security of the state. The government cannot prevent individuals from owning guns, but it can regulate the sale and use of guns.
The debate over gun control is one of the most controversial issues in American politics. Gun control advocates argue that the government should regulate the sale and use of guns in order to reduce gun violence. Gun rights advocates argue that the government should not infringe on the right of individuals to keep and bear arms.
The Supreme Court has ruled that the Second Amendment protects an individual’s right to keep and bear arms for self-defense. However, the Court has also ruled that the government can regulate the sale and use of guns in order to protect public safety.
4. Amendment 3
Quartering of Soldiers
The Third Amendment to the Constitution prohibits the government from quartering soldiers in private homes without the consent of the owner. This amendment was adopted in response to the British practice of quartering soldiers in private homes during the American Revolution.
The Third Amendment has been interpreted to mean that the government cannot force individuals to house soldiers in their homes. However, the government can quarter soldiers in public buildings or in private homes with the consent of the owner.
The Third Amendment is an important protection against government overreach. It ensures that individuals are not forced to house soldiers in their homes against their will.
5. Amendment 4
Search and Seizure
The Fourth Amendment to the Constitution protects individuals from unreasonable searches and seizures. This amendment requires the government to obtain a warrant before searching a person or their property. The warrant must be supported by probable cause, which means that there is a reasonable belief that a crime has been committed.
The Fourth Amendment is an important protection against government overreach. It ensures that individuals are not subject to arbitrary searches and seizures.
The Supreme Court has ruled that the Fourth Amendment requires the government to obtain a warrant before searching a person or their property. However, the Court has also ruled that there are some exceptions to this rule, such as when the search is conducted with the consent of the individual or when there is probable cause to believe that a crime has been committed.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights serves to protect individual rights and liberties from government encroachment, ensuring that citizens are not subject to arbitrary or oppressive actions by the state.
How many amendments are there in the Bill of Rights?
There are ten amendments in the Bill of Rights, which were adopted in 1791 as part of the original Constitution.
What is the most important amendment in the Bill of Rights?
While all ten amendments are essential, the First Amendment, which protects freedom of speech, religion, and the press, is often considered the most fundamental.